What is a SCADA System and How Does It Work?
We get asked all the time, “What is SCADA and how does it work?” SCADA stands for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition. It is a type of control system designed to collect data from industrial equipment. In this article, we’ll provide you with a high-level introduction to SCADA systems, how they work, and how to get started implementing your SCADA solution.
You can also check out our Tech Edge video on SCADA below.
What is a SCADA system?
A SCADA system is a combination of hardware and software that enables industrial process automation by capturing Operational Technology (OT) real-time data. SCADA connects the sensors that monitor equipment like motors, pumps, and valves to an onsite or remote server.
A SCADA system empowers organizations to:
- Control processes locally or at remote locations
- Acquire, analyze and display real-time data
- Directly interact with industrial equipment such as sensors, valves, pumps, and motors
- Record and archive events for future reference or report creation.
Depending on the configuration of the SCADA control system, the state of the industrial processes can be viewed from an operator workstation overlooking the industrial plant, a HMI located directly beside machinery, or even from the home of an employee.
To learn more about SCADA, download our eBook – The Ultimate Guide to Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition
SCADA system hardware
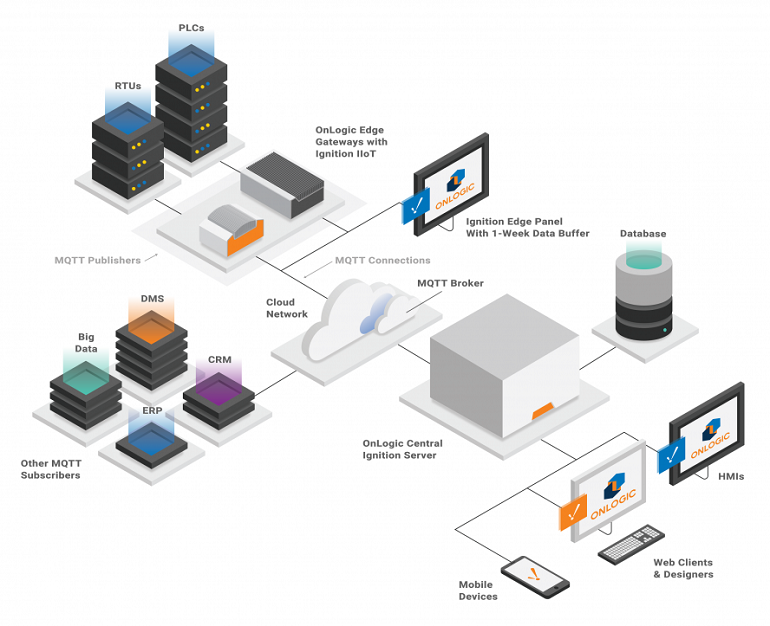
SCADA hardware, such as Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) and Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), serve as local collection points for acquiring sensor information. This hardware in a modern SCADA system will often trigger actions of the connected piece of equipment via programmed logic. In a SCADA system, the collected data from the sensors is gathered by a computer commonly known as a “gateway.”
Different edge workloads use computer hardware in various ways.
- Gateways pass the data from PLCs to servers or to the edge.
- Edge computers are close to the source of the data and can act as a gateway. However, they will first process the data before transferring to the cloud or central physical server. This enables quicker decisions at a local level as well as bandwidth and cost savings.
- Human Machine Interfaces (HMIs) provide a local touchscreen interface for machine monitoring and control. They can also act as gateways or edge computers.
- The server acts as the central control for your local SCADA system. Your local historian server (historical data logging over time) may live here. Depending on the architecture it may also report back to cloud or a larger server on the enterprise network
Once collected, sensor data can either be acted upon directly through the use of SCADA software, or saved for later review. SCADA systems can help monitor and control processes from the same location in which actions are performed, or from a remote site.
SCADA system examples
SCADA provides real-time visibility into on-premise operations, and helps business owners and operators to make more informed decisions, improving efficiency and minimizing downtime. But how is SCADA used for real-world applications? Let’s take a look at some common use-cases.
Oil and gas
SCADA is widely used in the oil and gas industry for industrial process automation. With the cost of unplanned downtime potentially reaching over $1 million for just one hour, having the right solution in place is critical. With a SCADA solution, businesses can have more insight into things like tank levels, temperature, pressure, and flow without needing to be on site. This information can then be acted upon automatically.
For example, with a SCADA system, if sensors read that the pressure in a well has started to build to unsafe levels, an alert can be sent out and systems can automatically shut off. Not only is this visibility vital in ensuring on-site personnel’s safety, but it can help to prevent costly downtime and save resources.
Smart cities
From wastewater treatment to power grid management, smart cities are increasingly relying on SCADA control systems to help monitor and optimize everything from traffic light patterns to public power consumption. When a city is able to see spikes in resource usage, such as public transit or electrical consumption, they are able to more quickly respond.
Cities can optimize resources over the long term when repeated trends are recognized. For example, certain temperatures and humidity levels may directly correlate with residents turning on their heating or cooling systems. City managers can prepare the grid to increase electrical production and transfer as those conditions develop.
At a more granular level, the increasing number of electric vehicles being charged is likely to have a growing impact on city electric grids. SCADA systems are one way to help monitor and adjust to evolving demands for power such as this.
Smart manufacturing
Modern factories use SCADA to monitor data from machinery sensors to predict maintenance, monitor output speed, and increase operator safety. For example, let’s say that data indicates that the rotating bit on a plywood cutting machine is vibrating excessively. The SCADA software can be programmed to power down the machine immediately and avoid potential harm to materials or operators.
Another example is using SCADA for predictive maintenance. A piece of equipment may become less efficient at a certain point in its maintenance cycle. With a SCADA system, you could recognize this pattern and change the maintenance schedule to avoid a production bottleneck. Without a SCADA system, it would be difficult to recognize such patterns manually.
With SCADA, production facilities can choose a hybrid version of direct and automated control by creating rules. The system can automatically respond to abnormal data, or it could alert an operator to the abnormal operation who can then make an informed decision on the appropriate next steps.
How to implement a SCADA solution
To successfully implement a SCADA solution, follow these steps:
- Clearly define and understand what you want to monitor
- Determine the data you currently collect and how
- Start small: pick one set of data and one location to do a proof of concept (POC)
- Define scalable architecture
- Add gateways to connect current data collection points
- Create new data collection points if desired
- Centralize your data to your intended monitoring location
- Map data in your SCADA software of choice
- Add visualizations of data and controls
- Define automations and rules
SCADA software then takes over to help you interact with your facility, alert you to issues, inform predictive maintenance, and provide control over a handful, or even thousands of pieces of equipment.
It may seem complicated at first, but the goals are simple. First, connect the things you want to monitor. Then, select the location from which you wish to monitor and control them.
Integrated SCADA software
With the amount of data being produced in modern industrial facilities, the opportunity for optimization has never been greater. The concept of collecting and acting on data isn’t new. But, today’s SCADA solutions offer incredible insights and capabilities that were previously inaccessible.
OnLogic partners with the SCADA experts at Inductive Automation. They created the popular and powerful Ignition SCADA software which was specifically developed to streamline modern industrial automation implementations. Our line of Ignition-ready edge gateways offer you a solid foundation to get up and running with a powerful, modern SCADA solution.
Still have questions about SCADA? Contact our team of experts for help today.
We originally posted this blog on December 1st, 2021. We updated the content on September 18th, 2023.
Editor’s Note: Inductive Automation has ended their Ignition Onboard program. Ignition licenses must now be purchased directly through Inductive Automation. While the IGN versions of our solutions are no longer available, our computers remain a great fit for use with Ignition software. Explore our recommended hardware here.
Get the Latest Tech Updates
Subscribe to our newsletters to get updates from OnLogic delivered straight to your inbox. News and insights from our team of experts are just a click away. Hit the button to head to our subscription page.
Share
More Articles
OnLogic Industrial Computers
Discover OnLogic's multitude of industrial computers that will help you to advance your IoT project
Learn more at OnLogic.com
OnLogic Industrial PCs: Designed to last. Built to order. Delivered in days. Visit our online store at OnLogic.com